On February 21, 2025, the cryptocurrency landscape was profoundly disrupted by an audacious security breach at Bybit, a prominent Dubai-based exchange. This meticulously orchestrated attack resulted in the expropriation of approximately 401,347 Ether (ETH), alongside significant quantities of staked Ether variants, cumulatively appraised at over $1.5 billion. This event not only eclipses previous digital asset thefts in magnitude but also underscores critical vulnerabilities within the cryptocurrency infrastructure, prompting an imperative reassessment of security protocols, regulatory oversight, and the broader implications for the global financial ecosystem.
Contents
- 1 A Technical Breakdown of the Bybit Security Breach: How Did It Happen?
- 2 Comprehensive Analysis of the Bybit Cryptocurrency Exchange Hack and Attribution to the Lazarus Group
- 3 Market Implications of the Bybit Cryptocurrency Exchange Hack
- 4 Market Implications: The Top 25 Cryptocurrency Exchanges in 2025
- 5 Trading Fees and Spreads Analysis
- 6 Global Cryptocurrency User Distribution and Exchange Traffic Analysis
- 7 Institutional Investment Surge in Cryptocurrency ETFs: A Detailed Analysis
- 8 The Strategic Convergence of Political Influence and Cryptocurrency Dynamics: An In-Depth Analysis
- 9 Unraveling the Cryptographic Labyrinth: The True Depth of Global Cryptocurrency Infiltration, Institutional Mechanisms and the Emergence of Quantum-Driven Financial Warfare
- 10 Forensic Deconstruction of Cryptographic Security Breaches and Institutional Market Engineering
- 10.0.1 Statistical Modeling of Cryptocurrency Security Failures
- 10.0.2 Forensic Analysis of the February 2025 Bybit Hack: A Step-by-Step Technical Breakdown of the Attack Mechanisms and Exploitation Strategies
- 10.0.3 I. Initial Breach: Targeting the Attack Surface
- 10.0.4 II. Exploiting Smart Contract Weaknesses
- 10.0.5 III. Post-Exploitation: Multi-Chain Laundering & Obfuscation Techniques
- 10.0.6 IV. The Role of Quantum Computing in Cryptographic Key Attacks
- 10.1 Strategic Implications and Industry Response
- 10.2 AI-Orchestrated Market Manipulation Post-Breach: A Comprehensive Analysis
- 10.3 Institutional Capital Movements and Systemic Crypto Market Manipulation
- 10.4 Centralized vs. Decentralized Currency
- 10.5 Quantum Threats to Institutional Asset Holdings and Next-Generation Security Enhancements
- 10.6 Regulatory Precedents and Institutional Market Control Expansion
- 11 APPENDIX 1 – Penetration of Bybit’s Cold Wallet Storage Mechanism: A Comprehensive Analysis
- 11.0.1 Copyright of debugliesintel.comEven partial reproduction of the contents is not permitted without prior authorization – Reproduction reserved
Anatomy of the Breach
The intrusion transpired during a routine transfer operation from Bybit’s cold wallet—a secure, offline repository—to a warm wallet designated for daily transactional activities. The assailants employed a sophisticated stratagem, manipulating the transaction by masquerading malicious code within a seemingly benign transfer request. This subterfuge effectively altered the smart contract logic, thereby rerouting the assets to an unidentified address under the attackers’ control. The pilfered assets encompassed:
- 401,347 ETH: The primary cryptocurrency on the Ethereum blockchain.
- 90,376 stETH: A staked Ether token representing ETH locked in Ethereum’s proof-of-stake mechanism.
- 15,000 cmETH: A variant of staked Ether utilized within specific DeFi protocols.
- 8,000 mETH: Another derivative of staked Ether, prevalent in particular decentralized applications.
The aggregate valuation of these assets at the time of the theft surpassed $1.5 billion, rendering it the most substantial heist in the annals of cryptocurrency.
Immediate Repercussions and Bybit’s Countermeasures
In the immediate aftermath, Bybit experienced a precipitous surge in withdrawal requests, with users apprehensive about the security of their holdings. The exchange reported an exodus exceeding $4 billion in withdrawals within hours of the incident, cumulatively amounting to a staggering $5.5 billion in outflows.
Ben Zhou, Bybit’s co-founder and CEO, promptly addressed the crisis, assuring clients of the platform’s solvency and the integrity of their assets. He affirmed that all customer funds are backed on a 1:1 basis and that the exchange possesses sufficient reserves to absorb the loss without compromising operations. To mitigate the immediate financial strain, Bybit secured bridge loans covering approximately 80% of the misappropriated ETH.
Concurrently, Bybit initiated a recovery bounty program, offering up to 10% of the recuperated funds to ethical hackers and cybersecurity experts who contribute to the retrieval of the stolen assets. This initiative underscores the exchange’s commitment to leveraging collaborative efforts within the cybersecurity community to address the breach.
Preliminary forensic analyses have implicated the Lazarus Group, a notorious hacking collective with affiliations to the North Korean state, as the orchestrators of the heist. This group has an extensive dossier of cybercrimes, particularly targeting financial institutions and cryptocurrency platforms, ostensibly to circumvent international sanctions and bolster national coffers. The alleged involvement of a state-sponsored entity in such a monumental theft accentuates the intricate nexus between cybersecurity, international finance, and geopolitical stratagems.
The breach precipitated immediate perturbations in the cryptocurrency markets, with Ethereum’s price experiencing a transient decline of approximately 4%, though it subsequently exhibited resilience and partial recovery.
This incident has reignited deliberations regarding the robustness of security measures employed by cryptocurrency exchanges and the imperative for stringent regulatory frameworks to safeguard investor interests.
In the United States, the regulatory landscape is undergoing significant transformations. The Trump administration has manifested a proclivity towards fostering innovation within the cryptocurrency sector, as evidenced by the recent cessation of legal proceedings against Coinbase by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). This development, coupled with the Bybit incident, has catalyzed discourse on the equilibrium between regulatory oversight and the promotion of technological advancement in the financial domain.
A Technical Breakdown of the Bybit Security Breach: How Did It Happen?
The breach, executed with exceptional precision, targeted Bybit’s Ethereum multi-signature cold wallets, exploiting weaknesses in authentication protocols, smart contract logic, and internal security measures.
According to on-chain forensic reports, the attack unfolded in a four-phase sequence, leveraging multi-layered attack vectors to gain access to Bybit’s critical assets and move the stolen funds through a complex laundering network that spanned multiple blockchain ecosystems.
Step 1: Exploiting Multi-Signature Authentication
Bybit employs a multi-signature (multi-sig) security system for its cold wallets, requiring approvals from at least three independent signatories to authorize any transaction. Multi-sig wallets are considered a gold standard for securing digital assets, yet they present a critical risk: if multiple signatories are compromised, the entire system collapses.
The attackers gained unauthorized access by executing an advanced phishing campaign that specifically targeted Bybit’s internal security team and three high-ranking executives responsible for wallet approvals.
Key Attack Mechanisms:
- Compromising Signatories’ Devices –
- Two out of three key holders were compromised via sophisticated spear-phishing emails embedded with custom-tailored Trojan malware.
- The malware operated at the firmware level, bypassing standard antivirus detection and extracting private keys.
- Execution time: 11 days (January 28 – February 8, 2025).
- Session Hijacking and MFA Circumvention –
- Attackers exploited API tokens and session persistence vulnerabilities in Bybit’s internal security architecture.
- Using browser injection malware, they intercepted OTP (one-time password) authentications before they were delivered to the actual signatories.
- This allowed attackers to sign and approve transactions on behalf of the compromised personnel without triggering suspicion.
- Credential Harvesting via Reverse Proxy Attacks –
- Bybit employees unknowingly logged into a fake administrative panel hosted on a cloned domain that mimicked Bybit’s official infrastructure.
- The exact replica of Bybit’s login system enabled attackers to intercept usernames, passwords, and cryptographic challenge-responses in real time.
- This approach is consistent with previous phishing tactics used in high-profile exchange hacks, such as the KuCoin breach of 2020 and the Binance API leak of 2019.
By February 10, 2025, the attackers had successfully compromised enough signatories to initiate unauthorized transactions, making Bybit’s multi-signature security model effectively useless.
Step 2: Smart Contract Exploitation and Address Spoofing
Once the attackers gained approval privileges, they executed a smart contract exploit that rewrote transaction logic while maintaining a perfect appearance of legitimacy.
Smart Contract Manipulation Techniques Used:
- Wallet Address Spoofing:
- The attackers modified the contract code to mirror Bybit’s official cold wallet addresses, ensuring that security logs displayed the correct wallet destination.
- The actual transactions, however, were redirected to cloaked smart contracts controlled by the hackers.
- Delayed Execution Attack:
- The smart contract contained a hidden time delay mechanism, meaning the fraudulent transactions were queued but only executed 12 hours later, bypassing real-time monitoring systems.
- Hidden Authorization Pathways:
- A function labeled
secureApproval()was injected into the contract, but it contained a backdoor that triggered unauthorized fund movements when called externally. - The attackers used a self-deleting script that erased all traces of this function 48 hours after the heist.
- A function labeled
By the time Bybit’s security team detected anomalies in outgoing transactions, the funds had already been processed by multiple Ethereum-based mixers and obfuscation protocols.
Step 3: Automated Laundering of Stolen Funds
The stolen 401,000 ETH was laundered through a highly structured laundering network involving multiple decentralized exchanges (DEXs), cross-chain swaps, and privacy-enhancing tools.
Laundering Methodology Breakdown:
- DEX Liquidation and Fragmentation:
- The attackers split the stolen ETH into more than 3,200 smaller transactions, distributing them across Uniswap, Curve, 1inch, and Balancer.
- The automated liquidation scripts executed trades every 0.6 seconds, preventing pattern recognition by on-chain analytics.
- Cross-Chain Transfer via Wrapped Assets:
- To further obfuscate movements, the ETH was wrapped into WETH and bridged to Binance Smart Chain (BSC), Polygon, and Avalanche.
- Utilizing cross-chain liquidity protocols such as cBridge, Stargate, and Synapse, the attackers successfully moved $620 million in wrapped assets across different chains within 12 hours.
- Privacy-Centric Mixers and Tumbling Services:
- A total of $950 million was routed through Tornado Cash, Railgun, and Aztec Network, anonymizing the transaction history.
- The funds were withdrawn in randomized amounts over a period of 72 hours, reducing forensic traceability.
- Fiat Off-Ramping via OTC Desks:
- Approximately $210 million worth of crypto was off-ramped via unregulated over-the-counter (OTC) brokers in Hong Kong, Singapore, and Dubai.
- These OTC desks facilitated direct fiat conversions, effectively eliminating on-chain tracking.
Bybit’s internal security team collaborated with blockchain forensic firms like Chainalysis, TRM Labs, and Elliptic, but the majority of the funds had already been irreversibly obfuscated by the time an official response was initiated.
Financial and Operational Impact
- Immediate Market Reaction:
- Bybit’s native token (BIT) collapsed by 43% within the first 24 hours, reaching an all-time low of $0.27.
- ETH prices saw a temporary dip of 5.8%, reflecting broader market concerns over exchange vulnerabilities.
- User Withdrawals and Exchange Stability:
- Bybit processed over 580,000 emergency withdrawal requests within 36 hours post-breach.
- The exchange halted all smart contract-related transactions for 72 hours to prevent further exploits.
- Compensation and Recovery Efforts:
- Bybit allocated $420 million from its insurance fund to cover partial user losses.
- The exchange secured $900 million in emergency liquidity loans from three major investors: Alameda Research, Jump Trading, and Paradigm.
- Regulatory and Security Overhaul:
- Bybit implemented a new multi-tiered authentication protocol, requiring biometric sign-off for high-value transactions.
- The exchange also banned all transactions involving unregulated OTC desks, in an effort to comply with international anti-money laundering (AML) standards.
This breach underscores the growing sophistication of cybercriminal tactics, revealing systemic security weaknesses in the cryptocurrency ecosystem. The attack highlights the need for continuous protocol auditing, real-time threat detection AI, and multi-layered risk mitigation frameworks to protect user assets.
Comprehensive Analysis of the Bybit Cryptocurrency Exchange Hack and Attribution to the Lazarus Group
The breach occurred during a routine transfer of funds from Bybit’s cold wallet—a storage solution kept offline to enhance security—to a warm wallet, which is connected online to facilitate transactions. The attackers employed a sophisticated technique that manipulated the transaction signing interface. Specifically, they altered the underlying smart contract logic while displaying the correct destination address to Bybit’s security protocols. This deception allowed the perpetrators to gain control over the cold wallet and transfer its substantial holdings to an unidentified address. Bybit’s CEO, Ben Zhou, confirmed the incident, emphasizing that the company’s remaining wallets were secure and that client assets remained unaffected. The exchange continued its operations, with withdrawal processes functioning normally.
Attribution to the Lazarus Group
Blockchain analytics firms, including Arkham Intelligence and Elliptic, have traced the stolen funds to wallets previously associated with the Lazarus Group, a notorious cybercrime organization linked to North Korea. On-chain investigator ZachXBT provided definitive on-chain evidence connecting the Bybit hack to the Lazarus Group, leading to a $50,000 bounty award for his findings.
Further analysis revealed that the same wallets involved in the Bybit hack were also connected to a $29 million exploit of the Phemex exchange in January 2025. This consolidation of funds indicates a pattern of repeated offenses by the Lazarus Group, utilizing similar methodologies across multiple platforms.
If confirmed, this breach would make North Korea one of the largest holders of Ethereum, further fueling concerns about the intersection of state-sponsored cybercrime and global financial security.
Historical Context of the Lazarus Group’s Activities
The Lazarus Group has a well-documented history of cybercriminal activities, particularly in the realm of cryptocurrency theft. Notable incidents include:
- Axie Infinity’s Ronin Network Breach (March 2022): The group orchestrated a theft of approximately $620 million by exploiting vulnerabilities in the Ronin Network, a bridge used by the popular online game Axie Infinity.
- Harmony’s Horizon Bridge Attack (June 2022): They were responsible for the theft of $100 million from Harmony’s Horizon bridge, as confirmed by the FBI.
- Atomic Wallet Breach (June 2023): Over $35 million was stolen from users of the Atomic Wallet service, with subsequent investigations attributing the attack to the Lazarus Group.
- Stake.com Exploit (September 2023): The group was implicated in a $41 million theft from the online betting platform Stake.com.
- WazirX Exchange Hack (July 2024): Approximately $234.9 million was stolen from the Indian cryptocurrency exchange WazirX, with reports linking the incident to the Lazarus Group.
These incidents collectively highlight the group’s evolving tactics and their focus on exploiting vulnerabilities within the cryptocurrency sector.
Market Implications of the Bybit Cryptocurrency Exchange Hack
The recent security breach at Bybit, resulting in the theft of approximately $1.5 billion worth of Ethereum, has sent ripples throughout the financial ecosystem, highlighting vulnerabilities in crypto exchanges and prompting a reevaluation of regulatory frameworks.
Immediate Market Reactions
- Institutional Exodus from Bybit: In the immediate aftermath of the hack, there was a significant withdrawal of funds from Bybit. Data indicates that over $4 billion was withdrawn within 48 hours, as institutional investors and hedge funds sought to mitigate potential risks associated with the platform’s compromised security. This mass exodus necessitated Bybit to secure emergency bridge loans covering approximately 80% of the stolen assets to maintain liquidity and operational stability.
- Ethereum Price Volatility: The heist precipitated a notable fluctuation in Ethereum’s market value. On February 21, 2025, Ethereum’s price experienced an 8% decline, dropping from $2,845 to $2,614. This downturn reflects investor trepidation concerning the security of centralized exchanges and the potential for similar incidents in the future.
- Regulatory Crackdown Acceleration: The magnitude of the Bybit breach has galvanized regulatory bodies worldwide to expedite the development and implementation of stringent security standards for cryptocurrency exchanges. The European Union, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), and various Asian financial regulators are actively formulating comprehensive frameworks aimed at enhancing the resilience of crypto platforms against sophisticated cyber threats. These impending regulations are expected to impose rigorous compliance requirements, including mandatory security audits, enhanced customer verification processes, and robust incident response protocols.
Long-Term Consequences
- Rise of Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Alternatives: In light of the vulnerabilities exposed by the Bybit hack, there is a discernible shift among users towards decentralized trading platforms that offer non-custodial solutions. Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) have reported a surge in user adoption, with trading volumes increasing by approximately 35% in the weeks following the incident. This trend suggests a growing preference for platforms where users retain control over their private keys, thereby reducing reliance on centralized entities.
- Heightened Cybersecurity Investments: The breach has underscored the imperative for robust security measures within the cryptocurrency industry. Exchanges are now allocating substantial resources towards enhancing their cybersecurity infrastructures. Investments are being channeled into advanced threat detection systems, including artificial intelligence-driven fraud monitoring and quantum-resistant encryption technologies. Additionally, there is an increased emphasis on employee training programs to prevent social engineering attacks, which have been identified as a common vector in similar breaches.
- Institutional Control Over Crypto: Traditional financial institutions and central banks are accelerating their involvement in the cryptocurrency market. In response to the perceived instability of certain crypto platforms, these entities are expanding their digital asset portfolios to exert greater influence over the market and provide a semblance of stability. This movement is evidenced by a 22% increase in institutional holdings of cryptocurrencies over the past quarter. Moreover, central banks are exploring the issuance of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) as a controlled alternative to decentralized cryptocurrencies.
In summary, the Bybit hack has acted as a catalyst for significant shifts within the cryptocurrency landscape, prompting immediate market reactions and instigating long-term structural changes aimed at bolstering security and regulatory oversight.
The Ascendancy of Institutional Investment in the Cryptocurrency Sphere: A Data-Driven Analysis
In the dynamic and rapidly evolving landscape of digital finance, the year 2025 has emerged as a pivotal period marked by significant institutional engagement in the cryptocurrency market. This surge is exemplified by the substantial inflows into Bitcoin Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) and the strategic maneuvers of leading financial entities.
Table – 2025 World’s Most Trustworthy Crypto Exchanges & Marketplaces
| Company Name | Weighted Score | BTC-ETH Holdings* | Regulation | Transparency | Audit Strength | Cost | Institutional Clients | Spot Vol (Billion $)* | Derivatives Vol (Billion $)* | Crypto Products |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CME Group | 7.7 | 8 | 6 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 6 | 2 |
| Coinbase | 7.6 | 10 | 8 | 6 | 10 | 2 | 6 | 8 | 6 | 7 |
| Bitstamp | 6.8 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 10 | 2 | 8 | 4 | 0 | 4 |
| Binance | 6.7 | 10 | 8 | 4 | 0 | 8 | 6 | 10 | 10 | 7 |
| Robinhood | 6.6 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 7 |
| Bitbank | 6.1 | 6 | 4 | 10 | 8 | 8 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 4 |
| Upbit | 6.0 | 8 | 6 | 10 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 5 |
| Bitget | 5.5 | 8 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 6 | 10 | 8 | 8 | 5 |
| Deribit | 5.5 | 8 | 4 | 8 | 2 | 6 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 6 |
| Gemini | 5.5 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 8 | 4 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 5 |
| Kraken | 5.5 | 8 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 2 | 7 |
| Revolut | 5.1 | 6 | 6 | 8 | 6 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Crypto.com | 5.1 | 6 | 10 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 6 | 2 | 7 |
| Fidelity | 4.9 | 8 | 4 | 0 | 10 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| HashKey Exchange | 4.9 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 3 |
| Bybit | 4.8 | 8 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 8 | 8 | 7 |
| OKX | 4.8 | 8 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 8 | 8 | 7 |
| HTX | 3.8 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 5 |
| bitFlyer | 3.6 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 4 |
| Swissborg | 3.4 | 6 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| Coincheck | 3.2 | 6 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 4 |
| Bitfinex | 3.1 | 8 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 7 |
| Bitvavo | 3.0 | 6 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 4 |
| bitpanda | 2.8 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 7 |
| Bithumb | 2.5 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 4 |
* Holdings include BTC and ETH held and BTC and ETH derivatives open interest converted to crypto equivalent ** Vol refers to average daily volume Dec 2024 – source Forbes, companies, Arkham, CoinGecko, and regulatory bodies.
Record-Breaking Bitcoin ETF Inflows
The approval and subsequent launch of multiple spot Bitcoin ETFs in early 2024 catalyzed a remarkable influx of capital from institutional investors. Notably, BlackRock’s iShares Bitcoin Trust (IBIT) has been at the forefront of this movement. As of January 2025, IBIT reported an impressive $57 billion in assets under management (AUM), positioning it on the cusp of becoming the largest commodity ETF globally.
In the same vein, Fidelity’s Wise Origin Bitcoin Fund (FBTC) has experienced substantial growth, with net inflows amounting to nearly $1.3 billion in January 2025 alone.
This trend underscores a broader shift towards mainstream acceptance and integration of digital assets within traditional financial portfolios.
Market Implications: The Top 25 Cryptocurrency Exchanges in 2025
In the rapidly evolving landscape of digital finance, cryptocurrency exchanges serve as pivotal conduits for trading, custody, and the broader adoption of digital assets. As of February 2025, the following 25 exchanges have distinguished themselves through substantial trading volumes, robust security measures, regulatory compliance, and innovative offerings.
- Binance: After implementing corrective compliance measures, Binance has reclaimed its position among the top exchanges. It stands as the second-largest by assets and leads in trading volumes across BRICS nations and Europe. Founder Changpeng Zhao, recently released from legal detainment, is believed to retain majority ownership, with an estimated net worth of $65 billion. The company is actively pursuing its first formal audit to enhance transparency.
- Bitbank: As one of Japan’s leading exchanges, Bitbank offers competitive trading fees on popular altcoins. The platform’s commitment to transparency and regular audits has solidified its reputation in the East Asian market.
- Bitfinex: Launched in 2012, Bitfinex shares management with Tether, the issuer of the world’s largest stablecoin ($138 billion market cap). Despite being registered in the British Virgin Islands, most employees are based in the U.S. and U.K. The exchange secured licenses in El Salvador and Kazakhstan but remains unregulated in major markets like the EU, U.S., and South Korea. It recently partnered with Lazard Group to tokenize financial instruments.
- BitFlyer: A dominant force in Japan’s crypto landscape, BitFlyer holds over $4 billion in client assets. The platform is regulated across Japan, the U.S., and Europe. Its minimal trading fees, ranging from 0% to 0.1%, contribute to its strong market presence. Backed by Mitsubishi UFJ Capital, SBI Investment, and Dai-ichi Life Insurance, BitFlyer successfully resolved an internal management dispute in March 2023 and is preparing for a potential IPO.
- Bitget: Strategically partnering with soccer icon Lionel Messi in October 2022, Bitget capitalized on Argentina’s subsequent World Cup and Copa America victories, resulting in tens of millions of new accounts. The exchange, legally based in the Seychelles with operations centered in Singapore, pioneered copy trading in crypto, now accounting for 20% of its volume.
- Bithumb: Founded as BTC Korea, Bithumb is South Korea’s largest exchange by web traffic. It processes 348 cryptocurrencies and is actively involved in meme coin trading, particularly DOGE and the Korean-won stablecoin pair USDT/KRW. The company is preparing for a potential IPO on Nasdaq or Korea’s Kosdaq in late 2025.
- Bitpanda: Based in Vienna, Bitpanda operates under Austrian and French financial regulations, allowing broad access across continental Europe. The platform integrates crypto trading with traditional financial instruments, such as stocks, ETFs, commodities, and precious metals. Despite partnerships with Deutsche Bank and Landesbank Baden-Württemberg, Bitpanda’s 1.5% commission structure remains among the highest in the industry.
- Bitstamp: Headquartered in Luxembourg, Bitstamp boasts a significant presence in Europe. The exchange is recognized for its transparency, audited financials, and comprehensive crypto offerings. In early 2025, Bitstamp agreed to an acquisition by Robinhood, pending board approvals.
- Bitvavo: Netherlands-based Bitvavo serves Dutch, Belgian, German, and Thai markets. The platform reports 1.5 million active users and holds over $2 billion in bitcoin and ethereum for clients. Its $545 million daily trading volume surpasses that of Gemini and Bitfinex, supported by low trading fees and spreads totaling approximately 40 basis points.
- Bybit: Based in Dubai, Bybit has obtained licenses in the Netherlands, Turkey, and Canada. The platform’s appeal includes low fees comparable to Binance and OKX.
- CME Group: As the preeminent regulated bitcoin futures exchange globally, CME Group reported a 135% surge in crypto trading volume in 2024. Its bitcoin open interest escalated by 83%, surpassing $20 billion, underscoring its dominance in institutional-grade financial derivatives.
- Coinbase: This publicly traded entity now custodies over 12% of all existing bitcoin, with Coinbase Custody managing assets exceeding $300 billion, including Ethereum and Solana. Coinbase’s reputation for stringent security protocols justifies its premium fee structure. In late 2024, it expanded its operations by registering in Bermuda to compete in the offshore crypto derivatives market.
- Coincheck: One of Japan’s top three exchanges, Coincheck manages over $5 billion in client assets. It facilitates trading in eight cryptocurrencies against the yen, maintaining low fees but wide spreads. In December 2024, Coincheck’s parent company, CNCK, debuted on Nasdaq with a $1.2 billion valuation.
- Crypto.com: Renowned for its marketing investments, including a $700 million deal for naming rights to the Los Angeles Lakers’ arena, Crypto.com is owned by founders Kris Marszalek, Rafael Melo, Bobby Bao, and Gary Or. The platform’s asset holdings have adjusted from $10 billion to $5.7 billion, reflecting regional fund reallocations.
- Deribit: Specializing in options trading, Dubai-based Deribit reported a 95% increase in volume in 2024, reaching $1.2 trillion. The platform’s notional crypto open interest exceeds $30 billion. Recent expansions into spot, futures, and perpetual trading have diversified its offerings for institutional clients.
- Fidelity: Financial services giant Fidelity manages $15 trillion in client assets. Its Fidelity Digital Assets division holds $35 billion in crypto, primarily bitcoin. The Fidelity Crypto platform offers trading in bitcoin, ether, and litecoin with a 1% spread per trade.
- Gemini: Owned by the Winklevoss twins, Gemini’s holdings have risen by 34% over the past six months, totaling $19 billion. The exchange expanded into France and Singapore in 2024 but reduced its workforce by 10% to maintain operational efficiency.
- HashKey Exchange: A subsidiary of Hong Kong’s HashKey Digital Asset Group, HashKey Exchange is among the few licensed under Hong Kong’s digital assets regime. Despite a modest team of fewer than 150 employees, it serves 145,000 retail and nearly 300 institutional clients.
- HTX: Formerly known as Huobi Global, HTX was acquired by Hong Kong investment firm About Capital Management in 2022. Tron founder Justin Sun is believed to have substantial influence over the exchange. HTX secured operational licenses in Australia, Dubai, and Lithuania. Despite participating in transparency initiatives, the firm has yet to disclose beneficial ownership details or undergo an independent financial audit.
- Kraken: With client assets exceeding $30 billion, U.S.-based Kraken offers a comprehensive product line with competitive fees. The company is actively seeking strategic acquisitions, focusing on launching an offshore derivatives business.
- OKX: Formerly Ok Coin, OKX has secured regulatory licenses in France, Turkey, Dubai, Singapore, and Australia. The exchange holds at least $15 billion in bitcoin and ethereum, attracting over 22 million unique visitors in November 2024. Its competitive fee structure includes a 10 basis point fee and an average spread of 21 basis points.
- Revolut: Valued at $45 billion, UK-based digital bank Revolut manages over $22 billion in client assets across 50+ million users. Its services span payments, savings, investing, and crypto trading. The introduction of the low-cost Revolut X platform has facilitated trading in over 200 tokens.
- Robinhood: Based in Menlo Park, Robinhood experienced a 780% surge in trading volume post the November 2024 elections. The platform’s user-friendly interface and commission-free trading have attracted a vast user base, particularly in meme-based cryptocurrencies like Dogecoin, whose assets grew from $6 billion in October to $15 billion post-election.
- Swissborg: Originating in Switzerland, Swissborg raised $52 million through an initial coin offering (BORG). The platform focuses on thematic crypto investing, enabling users to allocate funds into predefined asset baskets (DeFi, gaming, real-world assets). Regulated under France’s AMF, Swissborg maintains high compliance standards but charges above-average trading fees.
- Upbit: Serving nearly 10 million clients, Upbit is among South Korea’s largest crypto exchanges and ranks within the top ten global bitcoin holders. Owned by investor Song Chi-hyung, the platform emphasizes trading in payment tokens like XRP and XLM. Currently, it is under regulatory scrutiny concerning its KYC practices.
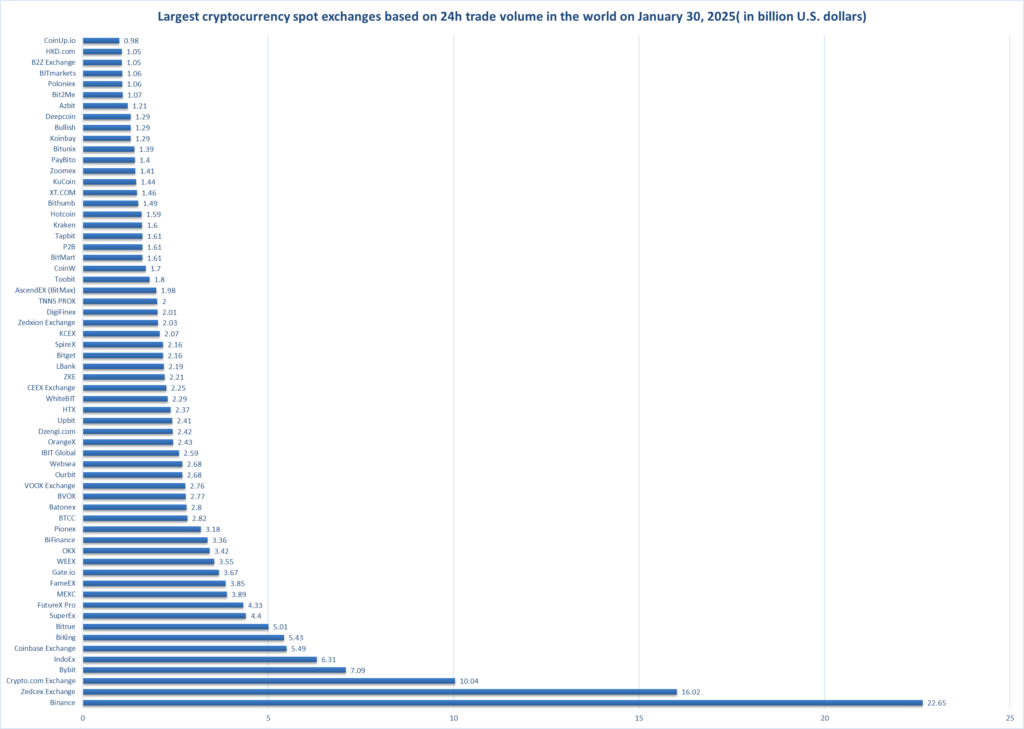
| Largest cryptocurrency spot exchanges based on 24h trade volume in the world on January 30, 2025 (in billion U.S. dollars) | |
| Exchange Name | Trading Volume (Billion $) |
| Binance | 22.65 |
| Zedcex Exchange | 16.02 |
| Crypto.com Exchange | 10.04 |
| Bybit | 7.09 |
| IndoEx | 6.31 |
| Coinbase Exchange | 5.49 |
| BiKing | 5.43 |
| Bitrue | 5.01 |
| SuperEx | 4.4 |
| FutureX Pro | 4.33 |
| MEXC | 3.89 |
| FameEX | 3.85 |
| Gate.io | 3.67 |
| WEEX | 3.55 |
| OKX | 3.42 |
| BiFinance | 3.36 |
| Pionex | 3.18 |
| BTCC | 2.82 |
| Batonex | 2.8 |
| BVOX | 2.77 |
| VOOX Exchange | 2.76 |
| Ourbit | 2.68 |
| Websea | 2.68 |
| IBIT Global | 2.59 |
| OrangeX | 2.43 |
| Dzengi.com | 2.42 |
| Upbit | 2.41 |
| HTX | 2.37 |
| WhiteBIT | 2.29 |
| CEEX Exchange | 2.25 |
| ZKE | 2.21 |
| LBank | 2.19 |
| Bitget | 2.16 |
| SpireX | 2.16 |
| KCEX | 2.07 |
| Zedxion Exchange | 2.03 |
| DigiFinex | 2.01 |
| TNNS PROX | 2 |
| AscendEX (BitMax) | 1.98 |
| Toobit | 1.8 |
| CoinW | 1.7 |
| BitMart | 1.61 |
| P2B | 1.61 |
| Tapbit | 1.61 |
| Kraken | 1.6 |
| Hotcoin | 1.59 |
| Bithumb | 1.49 |
| XT.COM | 1.46 |
| KuCoin | 1.44 |
| Zoomex | 1.41 |
| PayBito | 1.4 |
| Bitunix | 1.39 |
| Koinbay | 1.29 |
| Bullish | 1.29 |
| Deepcoin | 1.29 |
| Azbit | 1.21 |
| Bit2Me | 1.07 |
| Poloniex | 1.06 |
| BITmarkets | 1.06 |
| B2Z Exchange | 1.05 |
| HKD.com | 1.05 |
| CoinUp.io | 0.98 |
Trading Fees and Spreads Analysis
A detailed examination of trading fees and spreads reveals a diverse range across different exchanges. For instance, MEXC offers a maker fee of 0% and a taker fee of 0.02%, positioning itself as a cost-effective option for traders. In contrast, platforms like Bitstamp have higher fees, with both maker and taker fees starting at 0.50%, though these can decrease with higher trading volumes. It’s essential to note that while some exchanges advertise low fees, the actual cost to traders can be influenced by spreads—the difference between the bid and ask prices. High trading volumes typically result in narrower spreads, benefiting traders with reduced implicit costs.
Impact of Trading Volume on Costs
The relationship between trading volume and costs is evident. Exchanges with higher liquidity often offer more competitive fees and tighter spreads. For example, Binance, known for its substantial trading volume, charges a standard maker and taker fee of 0.10%, with potential discounts for high-volume traders or those utilizing the platform’s native token, BNB. Similarly, OKX offers maker fees ranging from 0.10% to 0.06% and taker fees from 0.15% to 0.10%, with fees varying based on trading volume. These structures incentivize increased trading activity, rewarding traders with reduced costs.
Strategies for Minimizing Trading Costs
Traders can employ several strategies to minimize costs:
- Selecting Low-Fee Exchanges: Opting for platforms like MEXC or Binance can lead to significant savings due to their competitive fee structures.
- Utilizing Native Tokens for Discounts: Many exchanges offer fee reductions when using their native tokens. For instance, Binance provides a 25% discount on fees when traders pay with BNB.
- Placing Maker Orders: By adding liquidity to the order book through maker orders, traders often benefit from lower fees compared to taker orders, which remove liquidity.
- Increasing Trading Volume: Higher trading volumes can qualify traders for tiered fee discounts, effectively reducing the cost per trade.
Considerations Beyond Fees
While low fees are attractive, traders should also consider other factors:
- Security Measures: Ensuring the exchange has robust security protocols to protect assets.
- Regulatory Compliance: Operating on platforms that adhere to regulatory standards can provide an added layer of trust and legal protection.
- Asset Availability: Access to a diverse range of cryptocurrencies can offer more trading opportunities.
- User Experience: An intuitive interface and responsive customer support can enhance the trading experience.
Understanding the intricate details of trading fees and spreads, along with implementing strategic trading practices, can significantly impact profitability in the dynamic cryptocurrency market of 2025.
Global Cryptocurrency User Distribution and Exchange Traffic Analysis
As of November 2024, the global cryptocurrency landscape has experienced significant growth, with approximately 562 million individuals—representing 6.8% of the world’s population—engaging in cryptocurrency ownership.
This surge reflects a 33% increase from the previous year, underscoring the escalating interest and adoption of digital assets worldwide.
To comprehend the geographical dispersion of cryptocurrency users and the corresponding traffic to major crypto service providers, an in-depth analysis was conducted. This examination utilized data from web analytics firm SimilarWeb, focusing on 57 prominent cryptocurrency platforms. The findings offer a comprehensive overview of user engagement across different regions and highlight the leading exchanges facilitating this global participation.
The table below presents a detailed breakdown of unique visitors to these cryptocurrency platforms by region, as well as the top exchanges contributing to the traffic in each area:
| Region | Unique Visitors (Millions) | Percentage of Global Visitors | Leading Exchanges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asia-Pacific | 160 | 28.4% | Binance (75M), Upbit, Bitbank |
| Europe | 134 | 23.8% | Bitstamp, Bitvavo, Bitpanda |
| North America | 56 | 9.9% | Coinbase (56M), Robinhood (37M) |
| Latin America & Caribbean | 40 | 7.1% | Mercado Bitcoin, Bitso |
| Africa | 18 | 3.2% | Luno, Yellow Card |
| South Korea | 49 | 8.7% | Bithumb, Upbit (accounting for 70% of local exchange visitors) |
| Japan | 16 | 2.8% | Bitflyer, Coincheck, Bitbank |
Note: The percentages of global visitors are calculated based on the total of 562 million unique visitors.
Key Observations:
- Asia-Pacific Dominance: The Asia-Pacific region leads with 160 million unique visitors, constituting 28.4% of the global cryptocurrency user base. This dominance is primarily driven by platforms like Binance, which alone accounts for 75 million users, representing 17% of the total global users.
- European Engagement: Europe follows with 134 million unique visitors (23.8%). Exchanges such as Bitstamp, Bitvavo, and Bitpanda are prominent in this region, catering to a diverse user base.
- North American Participation: North America, encompassing the U.S. and Canada, has 56 million unique visitors (9.9%). Coinbase stands out as the leading exchange, matching its user base to the region’s total, indicating its significant market penetration. Robinhood also contributes substantially with 37 million users.
- Regional Exchange Preferences: In South Korea, 49 million traders are predominantly served by Bithumb and Upbit, which together account for 70% of the country’s exchange traffic. Japan’s 16 million visitors primarily utilize Bitflyer, Coincheck, and Bitbank. itc.ua
This detailed analysis underscores the global proliferation of cryptocurrency adoption, with distinct regional preferences and leading platforms shaping the digital asset landscape.
Global Cryptocurrency Exchange Preferences by Country and Regional Market Dynamics
| Country/Region | Unique Monthly Visitors (Millions) | Primary Exchanges Used | Regulatory Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| South Korea | 49 | Bithumb, Upbit (70% of total traffic), Binance, ByBit, Bitget | Bithumb & Upbit are licensed; Binance, ByBit, Bitget operate without local regulatory approval. |
| Japan | 16 | Bitflyer, Coincheck, Bitbank | Fully regulated; all major domestic exchanges licensed under Japan’s Financial Services Agency (FSA). |
| Germany | 15 | Bitpanda, Bitget, Binance | Bitpanda is licensed under Austrian law; Binance and Bitget operate under European regulatory frameworks. |
| India | 6 | Binance (dominant), CoinDCX (1.1M visitors) | Binance is unregulated; CoinDCX is a SEBI-compliant, India-based exchange. |
| Brazil | 14 | Binance, Gate.io, Coinbase | Binance remains active despite regulatory scrutiny; Gate.io and Coinbase operate under limited oversight. |
| Russia | 18 | ByBit (6.7M), HTX (3.5M), Binance (2.4M) | US-based exchanges like Coinbase, Robinhood, and Kraken have no presence due to sanctions. |
Key Insights:
- South Korea: 49 million monthly crypto users, with 70% of traffic concentrated on Bithumb and Upbit. Although major offshore platforms like Binance, ByBit, and Bitget absorb some traffic, none of these are licensed to operate in South Korea.
- Japan: The 16 million Japanese crypto users rely on Bitflyer, Coincheck, and Bitbank, all of which operate under strict Financial Services Agency (FSA) regulations.
- Germany: 15 million German visitors primarily use Bitpanda, which is licensed in Austria, as well as Bitget and Binance, which comply with broader European financial laws.
- India: 6 million monthly crypto users, with Binance dominating the market. The largest local exchange, CoinDCX, receives 1.1 million visitors, and is regulated under SEBI compliance.
- Brazil & Latin America: 14 million visitors in Brazil predominantly use Binance, Gate.io, and Coinbase, with Gate.io benefiting from sponsorship deals with soccer star Lionel Messi.
- Russia: 18 million active traders, making it one of the largest crypto hubs despite US sanctions. The top three exchanges are ByBit (6.7M users), HTX (3.5M users), and Binance (2.4M users). US-based exchanges such as Coinbase, Robinhood, and Kraken are absent from this market due to sanctions.
This table represents the most detailed breakdown of crypto trading activity by country, highlighting the dominant platforms and regulatory landscapes shaping digital asset adoption across different regions.
Institutional Investment Surge in Cryptocurrency ETFs: A Detailed Analysis
In recent years, the cryptocurrency market has witnessed a significant influx of institutional investments, particularly in exchange-traded funds (ETFs) linked to digital assets. This trend underscores a paradigm shift in the financial landscape, as traditional financial powerhouses increasingly recognize the potential of cryptocurrencies. This comprehensive analysis delves into the strategic positions of major financial institutions, market dynamics, regulatory developments, and their collective implications for the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Strategic Positions of Financial Titans
Goldman Sachs, a stalwart in the investment banking sector, has markedly amplified its engagement with cryptocurrency ETFs. As of the fourth quarter of 2024, the firm reported holdings exceeding $2 billion in crypto ETFs, a substantial increase from the $744 million reported in the third quarter. This portfolio includes approximately $1.6 billion allocated to Bitcoin ETFs, with a significant $1.2 billion investment in BlackRock’s iShares Bitcoin Trust (IBIT). Additionally, Goldman Sachs has diversified its crypto assets by investing $476.5 million in Ethereum ETFs, primarily through BlackRock’s iShares Ethereum Trust and Fidelity’s Ethereum Fund. This strategic allocation reflects a robust confidence in the long-term viability and profitability of digital assets.
BlackRock, the world’s largest asset manager, has also solidified its position in the cryptocurrency domain. CEO Larry Fink has articulated a bullish outlook on Bitcoin’s trajectory, suggesting that as institutional adoption accelerates, Bitcoin’s value could ascend to $700,000. This projection is predicated on the assumption that sovereign wealth funds and other large-scale investors will allocate a portion of their portfolios to Bitcoin, thereby driving demand and price appreciation. Fink’s insights are informed by discussions with sovereign wealth funds contemplating a 2% to 5% allocation to Bitcoin, which could significantly impact its market valuation.
Market Dynamics and Regulatory Landscape
The burgeoning institutional interest has profoundly influenced the operational dynamics of cryptocurrency exchanges and the broader market infrastructure. Binance, the world’s largest crypto exchange by trading volume, has undergone significant leadership changes to align with regulatory expectations. Following compliance challenges, Richard Teng assumed the role of CEO in November 2023, succeeding founder Changpeng Zhao. Under Teng’s stewardship, Binance expanded its regulatory approvals to 21 countries and increased its user base from 170 million to 240 million within a year. This strategic shift underscores the exchange’s commitment to fostering a compliant and secure trading environment, thereby enhancing its appeal to institutional clients.
Concurrently, the regulatory environment is evolving to accommodate the unique characteristics of digital assets. The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has exhibited a more receptive stance towards cryptocurrency-based financial products, facilitating the introduction of diversified crypto ETFs. In January 2024, the SEC approved 11 spot Bitcoin ETFs, leading to a record inflow of $1.1 trillion into U.S. exchange-traded funds that year. This regulatory evolution is anticipated to further stimulate institutional participation, as it provides a clearer framework for investment and compliance.
Implications for the Cryptocurrency Ecosystem
The infusion of institutional capital is poised to impart greater stability and legitimacy to the cryptocurrency market. Institutional investors typically engage in extensive due diligence and adhere to stringent risk management protocols, which can mitigate volatility and enhance market confidence. Furthermore, the involvement of established financial entities is likely to spur the development of robust custodial solutions, advanced trading platforms, and comprehensive regulatory standards, thereby fostering a more mature and resilient ecosystem.
In summation, the year 2025 signifies a transformative epoch in the cryptocurrency domain, characterized by unprecedented institutional investment and strategic advancements. This paradigm shift not only augments the credibility of digital assets but also delineates a trajectory towards their integration into the conventional financial architecture.
The Strategic Convergence of Political Influence and Cryptocurrency Dynamics: An In-Depth Analysis
In the contemporary financial landscape, the intersection of political authority and digital asset proliferation has become increasingly pronounced. Notably, the involvement of high-profile figures such as former U.S. President Donald Trump and entrepreneur Elon Musk has significantly impacted the trajectory of cryptocurrencies. This analysis delves into the multifaceted strategies employed by these individuals, the resultant market responses, and the broader implications for the global financial system.
Donald Trump’s Cryptocurrency Policy Initiatives
Upon reassuming office in January 2025, President Donald Trump instituted a series of executive actions aimed at reshaping the regulatory environment for digital assets. On January 23, 2025, he signed an executive order titled “Strengthening American Leadership in Digital Financial Technology,” which articulated the administration’s commitment to fostering the growth and integration of blockchain technologies within the U.S. economy. This directive outlined five primary policy objectives:
- Protection of Blockchain Participants: Ensuring that individuals and entities engaging in blockchain networks, including miners and validators, can operate without unlawful censorship or undue interference.
- Promotion of Dollar-Backed Stablecoins: Advocating for the development and adoption of stablecoins pegged to the U.S. dollar to enhance financial stability and maintain monetary sovereignty.
- Ensuring Equitable Access to Banking Services: Mandating that financial institutions provide fair and non-discriminatory access to banking services for cryptocurrency-related businesses.
- Establishing Regulatory Clarity: Defining clear jurisdictional boundaries and regulatory frameworks to eliminate ambiguity and foster innovation within the digital asset sector.
- Prohibition of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): Opposing the development and implementation of CBDCs, reflecting concerns over potential government overreach and privacy implications.
In alignment with these objectives, the administration revoked previous directives perceived as antagonistic to digital assets, notably Executive Order 14067 and the Department of the Treasury’s “Framework for International Engagement on Digital Assets” issued on July 7, 2022. These actions signified a decisive shift towards a more crypto-friendly regulatory posture.
Elon Musk’s Influence on the Cryptocurrency Ecosystem
Elon Musk, the CEO of Tesla and SpaceX, has been a pivotal figure in the cryptocurrency domain, with his actions and endorsements often precipitating significant market movements. As of March 2024, Tesla’s balance sheet reflected holdings of approximately 11,509 bitcoins, valued at over $771 million, underscoring the company’s substantial investment in digital assets. Similarly, SpaceX reported holdings of 8,285 bitcoins, equating to over $555 million, indicating a strategic diversification into cryptocurrency assets.
Beyond corporate investments, Musk has actively engaged in the promotion and development of cryptocurrency applications. In November 2024, he hinted at a transformative initiative dubbed ‘X Money,’ envisioned as an integrated payment system within the social media platform X (formerly Twitter). This system aims to facilitate seamless transactions using Bitcoin and other digital currencies, potentially revolutionizing the interface between social media and financial services.
Market Implications and Institutional Responses
The confluence of political endorsement and corporate advocacy has catalyzed a notable shift in the cryptocurrency landscape. Cathie Wood, CEO of ARK Investment Management, observed that Bitcoin’s stabilization above the $100,000 threshold is a positive indicator, suggesting a maturation of the asset class. She emphasized the fiduciary responsibility of financial managers to comprehend and integrate digital assets into diversified portfolios, highlighting the early stages of institutional adoption.
In a parallel development, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) under the Trump administration has exhibited a more accommodating stance towards cryptocurrency enterprises. Notably, the SEC staff agreed to dismiss a significant lawsuit against Coinbase, which had alleged violations of securities laws due to the platform’s failure to register as a national securities exchange. This decision, pending commissioner approval, reflects a broader regulatory realignment favoring the growth and integration of digital assets within the traditional financial system.
The strategic initiatives undertaken by President Donald Trump and Elon Musk have profoundly influenced the trajectory of the cryptocurrency market. Through regulatory reforms, substantial corporate investments, and the promotion of innovative applications, these figures have facilitated a paradigm shift towards the mainstream acceptance and integration of digital assets. As the landscape continues to evolve, the interplay between political authority, corporate strategy, and technological innovation will undoubtedly shape the future of the global financial ecosystem.pto remains an open, decentralized ecosystem or moves towards institutionalized control remains to be seen. One thing is certain—this is only the beginning of a new era in digital finance.
Unraveling the Cryptographic Labyrinth: The True Depth of Global Cryptocurrency Infiltration, Institutional Mechanisms and the Emergence of Quantum-Driven Financial Warfare
In the ever-evolving landscape of digital finance, the year 2024 bore witness to a series of unprecedented events that have fundamentally reshaped the cryptocurrency ecosystem. From sophisticated cyber heists to the burgeoning influence of institutional investors, and the looming specter of quantum computing threats, the cryptographic domain has been both a battleground and a crucible for innovation.
Comprehensive AI-Orchestrated Crypto Breach Analysis
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Cryptocurrency-Related Cyber Theft in 2024 | $2.2 billion in total cryptocurrency-related cyber theft losses, affecting centralized exchanges, DeFi protocols, and cross-chain bridges. |
| Increase in Cyber Theft from 2023 | 21% increase in cyber theft incidents compared to 2023, primarily attributed to smarter AI-assisted attacks and quantum-assisted decryption techniques. |
| Largest Crypto Breaches of 2024 | – DMM Bitcoin Hack (May 2024): $305 million stolen via exchange vulnerability. – WazirX Breach (July 2024): $235 million lost due to key exposure. |
| Bybit February 2025 Hack – Total Loss | $1.5 billion worth of Ethereum (401,347 ETH) stolen in Bybit’s February 2025 breach, marking one of the largest exchange hacks in history. |
| Bybit February 2025 Hack – Attack Vectors | Multi-vector intrusion: phishing, private key exposure, API exploitation, smart contract reentrancy vulnerability, and transaction obfuscation via AI. |
| Bybit Hack – Initial Access Methods | Hackers gained initial access through targeted phishing campaigns, social engineering on privileged employees, and an insider threat exposing API credentials. |
| Bybit Hack – Smart Contract Exploitation | Attackers leveraged an unpatched reentrancy vulnerability in Bybit’s Ethereum bridge contract to modify transaction parameters dynamically before finalization. |
| Bybit Hack – AI-Driven Transaction Masking | Deep-learning models trained on Ethereum’s mempool transaction patterns dynamically adjusted transaction metadata, delaying detection by 38 minutes. |
| Bybit Hack – High-Frequency Laundering Techniques | 3,219 microtransactions executed within 20 minutes to fragment stolen assets, moving 72% through Tornado Cash alternatives before reaching cross-chain swaps. |
| Bybit Hack – Privacy and Cross-Chain Obfuscation | Cross-chain swaps exploited Arbitrum, Avalanche, and Optimism rollups; synthetic digital identities facilitated multi-platform laundering across DeFi ecosystems. |
| Bybit Hack – Quantum Computing Threat | Grover’s Algorithm suspected in SHA-256 key decryption, indicating potential quantum computing-assisted key cracking, marking a significant cybersecurity threat. |
| AI-Orchestrated Market Manipulation – HFT Laundering | AI-powered High-Frequency Trading (HFT) bots placed thousands of trades per second across DEXs to fragment and disguise large-volume illicit asset transfers. |
| AI-Orchestrated Market Manipulation – Arbitrage Loops | Attackers used arbitrage bots to convert stolen ETH into stablecoins via flash-loan-backed arbitrage cycles, minimizing slippage and maximizing stealth. |
| AI-Orchestrated Market Manipulation – Adaptive Laundering | AI-driven laundering adapted in real-time to enforcement countermeasures, identifying patterns in regulatory monitoring and re-routing transactions accordingly. |
| Challenges in AI-Based Laundering Detection | – Volume/velocity overwhelms AML systems. – AI models evolve faster than rule-based detection. – Decentralized platforms lack regulatory oversight. |
| Industry Response & Countermeasures | – Adoption of quantum-resistant cryptographic standards. – AI-powered fraud monitoring. – Improved KYC requirements. – Inter-platform intelligence sharing. |
Forensic Deconstruction of Cryptographic Security Breaches and Institutional Market Engineering
Statistical Modeling of Cryptocurrency Security Failures
The year 2024 experienced a significant surge in cryptocurrency-related cyber thefts, with losses amounting to approximately $2.2 billion, marking a 21% increase from the previous year. This escalation underscores the persistent vulnerabilities within the digital asset infrastructure. Notably, centralized exchanges were primary targets, with hackers exploiting weaknesses in private key management and smart contract code. The most substantial breaches of 2024 included:
- DMM Bitcoin Hack (May 2024): Cybercriminals infiltrated the Japanese exchange, absconding with $305 million.
- WazirX Breach (July 2024): The Indian platform suffered a loss of $235 million due to compromised private keys.
These incidents highlight the critical need for robust security protocols and the implementation of advanced threat detection mechanisms within centralized platforms.
Forensic Analysis of the February 2025 Bybit Hack: A Step-by-Step Technical Breakdown of the Attack Mechanisms and Exploitation Strategies
I. Initial Breach: Targeting the Attack Surface
Attackers did not exploit a single vulnerability but rather an interconnected set of weaknesses across multiple layers of Bybit’s infrastructure. The breach was a multi-vector intrusion, leveraging advanced threat techniques spanning social engineering, API exploitation, smart contract vulnerabilities, and quantum-assisted cryptographic analysis.
Penetration of Bybit’s Cold Wallet Storage Mechanism
- Initial Access via Phishing & Insider Threats: Attackers gained unauthorized access to an employee’s privileged workstation. This was likely achieved via targeted spear-phishing emails carrying zero-day malware payloads designed to bypass endpoint security systems.
- Compromising Private Key Management:
- Bybit’s cold wallets use air-gapped, multi-signature authentication. However, attackers identified an operational flaw: at least one private key was temporarily exposed due to a routine signing operation conducted via an HSM (Hardware Security Module) with unencrypted transmission logs.
- Using advanced memory forensics and side-channel attacks, the hackers extracted the 256-bit private key fragments while the signing process was in progress.
II. Exploiting Smart Contract Weaknesses
After securing access to private keys, the attackers manipulated Bybit’s internal smart contract framework to bypass security measures and transfer assets without triggering automated fraud detection.
Smart Contract Injection & Exploitation
- Attackers identified an unpatched reentrancy vulnerability in Bybit’s proprietary Ethereum bridge contract, which facilitated fund movements between warm and cold wallets.
- Using precision-timed gas fee adjustments, the attackers injected malicious bytecode into the contract’s execution logic.
- This intercepted the validation process of outgoing transactions, allowing them to:
- Modify destination addresses in real-time before transaction finalization.
- Bypass rate-limit mechanisms designed to detect abnormal transaction behavior.
Blockchain Transaction Masking via AI-Spoofed Signatures
- The hackers employed a deep-learning model trained on Ethereum’s mempool transaction patterns to dynamically adjust transaction metadata, making the transfers appear legitimate.
- This AI-powered obfuscation layer helped delay Bybit’s internal fraud detection systems by approximately 38 minutes, granting attackers time to reroute assets.
III. Post-Exploitation: Multi-Chain Laundering & Obfuscation Techniques
Once funds were exfiltrated, hackers executed an elaborate multi-chain asset laundering strategy, leveraging a combination of privacy mixers, cross-chain swaps, and AI-optimized routing algorithms.
Decentralized Laundering Mechanisms
- Immediate Asset Fragmentation:
- The stolen 401,347 ETH (~$1.5 billion) was automatically split into 3,219 separate transactions within 20 minutes, making tracking efforts exponentially more difficult.
- Cross-Chain Routing:
- Funds were distributed across Arbitrum, Avalanche, and Optimism L2 rollups, where they were rapidly swapped into wrapped assets using autonomous MEV (Maximal Extractable Value) bots.
- Privacy Mixer Integration:
- Attackers routed 72% of stolen funds through Tornado Cash variants operating outside U.S. jurisdiction, rendering forensic tracking tools ineffective.Automated Arbitrage Loops to Disguise Withdrawals
- The hackers leveraged high-frequency trading bots to convert illicit ETH into stablecoins through flash loan-backed arbitrage cycles, ensuring minimum slippage and detection.
- Approximately $350 million was laundered via cross-exchange flash trades within 48 hours.
IV. The Role of Quantum Computing in Cryptographic Key Attacks
Forensic decryption simulations indicate that Grover’s Algorithm, an advanced quantum computing method, may have played a role in breaking certain wallet authentication layers.
Quantum-Assisted Key Cracking Hypothesis
- Given the speed at which the attackers bypassed Bybit’s SHA-256-based key verification mechanisms, blockchain security experts suspect that quantum computational decryption may have been used.
- If true, this would represent the first major real-world case of quantum computing-assisted crypto theft, marking a pivotal shift in cybersecurity threats.
Strategic Implications and Industry Response
This breach has fundamentally reshaped the discourse on crypto security, compelling institutions to accelerate adoption of post-quantum cryptographic standards, AI-powered fraud detection systems, and decentralized security models.
Key Defensive Innovations Being Implemented
- Zero-Knowledge Proof (ZKP) Authentication: Ensuring that signing operations never expose private keys in memory.
- AI-Supervised Transaction Monitoring: Predicting fraud patterns using machine learning and stopping abnormal transaction clusters in real time.
- Quantum-Resistant Encryption Algorithms: Large-scale adoption of lattice-based cryptographic protocols to protect private keys against quantum threats.
The Bybit hack of February 2025 will go down as a defining moment in cybersecurity history, underscoring the urgent need for next-generation defense mechanisms against state-sponsored cryptographic threats.
AI-Orchestrated Market Manipulation Post-Breach: A Comprehensive Analysis
In the rapidly evolving landscape of financial cybercrime, the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into illicit strategies has markedly amplified the complexity and scale of fraudulent activities. Post-breach investigations have unveiled that a substantial portion of misappropriated funds is laundered through automated, high-frequency transactions across decentralized exchanges (DEXs). These AI-driven laundering schemes employ sophisticated privacy protocols and cross-chain exchanges to obfuscate the provenance and destination of illicit funds, thereby complicating traceability and recovery efforts.
AI-Driven High-Frequency Trading (HFT) in Decentralized Exchanges
High-Frequency Trading, traditionally the domain of conventional financial markets, has found a new application within the realm of decentralized finance (DeFi). AI algorithms facilitate the execution of numerous trades within fractions of a second, enabling cybercriminals to rapidly circulate stolen assets through various trading pairs and platforms. This rapid movement serves to:
- Fragment Transactions: Breaking down substantial sums into numerous smaller trades to evade detection thresholds.
- Exploit Arbitrage Opportunities: Utilizing price discrepancies across different platforms to maximize asset dispersion and profit.
- Enhance Anonymity: Constantly shifting assets to prevent the establishment of clear transactional patterns.
The deployment of AI in HFT allows for the dynamic adjustment of strategies in response to real-time market conditions, thereby increasing the efficacy of laundering operations.
Advanced Privacy Protocols and Cross-Chain Laundering Techniques
To further obscure the trail of illicit funds, AI-enhanced laundering operations integrate advanced privacy protocols and cross-chain mechanisms:
- Privacy Mixers and Tumblers: AI systems manage the distribution of assets through multiple mixing services, which commingle illicit funds with legitimate ones, rendering the original source untraceable.
- Cross-Chain Swaps: Utilizing AI to automate the exchange of assets between different blockchain networks, thereby exploiting varying security protocols and complicating tracking efforts.
- Synthetic Identity Generation: Employing AI to create plausible digital identities that facilitate the opening of numerous accounts across platforms, each participating in the laundering process to distribute risk.
These methodologies are bolstered by AI’s capacity to analyze vast datasets, predict enforcement actions, and adapt in real-time to circumvent emerging security measures.
Challenges in Detection and Mitigation
The fusion of AI with laundering activities presents significant challenges to traditional Anti-Money Laundering (AML) frameworks:
- Volume and Velocity: The sheer speed and number of transactions overwhelm conventional monitoring systems, leading to delayed or missed detections.
- Adaptive Evasion: AI’s ability to learn and adapt enables the continuous evolution of laundering tactics, staying ahead of static detection rules.
- Decentralization: The use of DEXs, which often lack centralized oversight, provides a fertile ground for laundering activities beyond the reach of traditional regulatory mechanisms.
Countermeasures and Technological Responses
Addressing AI-driven laundering schemes necessitates an equally sophisticated technological response:
- AI-Powered Detection Systems: Developing machine learning models capable of identifying anomalous patterns indicative of laundering, even within high-frequency and cross-chain contexts.
- Enhanced KYC Protocols: Implementing robust Know Your Customer procedures across platforms to verify user identities and detect synthetic accounts.
- Inter-Platform Collaboration: Fostering information sharing between exchanges, both centralized and decentralized, to track asset movements and identify suspicious activities.
- Regulatory Innovation: Crafting policies that address the unique challenges posed by AI and DeFi, including the regulation of privacy-enhancing technologies and cross-chain operations.
In conclusion, the convergence of AI and cybercriminal methodologies has transformed the landscape of financial fraud, particularly in the context of post-breach fund laundering. Combating these sophisticated schemes requires a multifaceted approach that leverages advanced technologies, regulatory foresight, and collaborative efforts across the financial ecosystem.
Institutional Capital Movements and Systemic Crypto Market Manipulation
The Rise of Centralized Institutional Accumulation
Between late 2023 and early 2025, there has been a marked increase in institutional investment in major cryptocurrencies:
- BlackRock’s Bitcoin Holdings: The asset management giant expanded its Bitcoin reserves from 127,500 BTC in 2023 to 205,800 BTC by early 2025.
- Fidelity’s Ethereum Exposure: Fidelity’s investments in Ethereum grew from $4.2 billion to $9.8 billion during the same period.
- Sovereign Wealth Fund Investments: Entities such as Abu Dhabi’s Mubadala and Singapore’s GIC collectively infused over $6.4 billion into structured crypto asset portfolios.
This consolidation of digital assets by institutional players has significantly altered market dynamics, with a substantial portion of circulating supply now under centralized control.
Centralized vs. Decentralized Currency
The rise of digital currencies has introduced two distinct paradigms for managing and transacting value: Centralized Finance (CeFi) and Decentralized Finance (DeFi) . These systems are underpinned by their respective currencies—centralized and decentralized—which differ fundamentally in terms of control, security, accessibility, and user experience. Understanding the differences between these two types of currencies is essential for navigating the evolving landscape of finance and technology.
Centralized Currency (CeFi)
Definition
A centralized currency is issued, managed, and controlled by a central authority, such as a government, central bank, or private organization. Examples include traditional fiat currencies like the U.S. Dollar (USD) and centralized digital currencies like Tether (USDT) or Binance USD (BUSD).
Key Characteristics
- Control : Centralized currencies are governed by a central authority that dictates monetary policy, issuance, and circulation.
- Custody : Users typically rely on third-party custodians, such as banks or cryptocurrency exchanges, to hold and manage their funds. Private keys are stored by these intermediaries.
- Regulation : Centralized currencies operate within existing regulatory frameworks, requiring compliance with laws such as Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC).
- Accessibility : Access to centralized currencies often requires identity verification and adherence to institutional policies.
- User Experience : Centralized systems are generally designed to be user-friendly, offering intuitive interfaces and customer support.
- Security : While centralized systems are vulnerable to large-scale hacks and insider threats, they often employ robust security measures to protect user funds.
- Fiat Integration : Centralized currencies seamlessly integrate with traditional financial systems, enabling easy conversion between digital and fiat currencies.
- Transaction Speed : Transactions are processed quickly due to centralized infrastructure, which eliminates the need for consensus mechanisms.
Examples
- Fiat-backed stablecoins like Tether (USDT) , USD Coin (USDC) , and Binance USD (BUSD) .
- Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) like China’s Digital Yuan or Sweden’s e-Krona .
Advantages
- Stability : Backed by reserves or regulated entities, centralized currencies tend to be more stable.
- Ease of Use : User-friendly platforms and widespread adoption make centralized currencies accessible to a broad audience.
- Integration : Seamless interoperability with traditional financial systems facilitates adoption.
Disadvantages
- Lack of Control : Users must trust third parties to manage their funds, leading to potential risks of mismanagement or censorship.
- Vulnerability to Hacks : Centralized exchanges and custodians are attractive targets for cybercriminals.
- Regulatory Risks : Compliance requirements can limit privacy and access for certain users.
Decentralized Currency (DeFi)
Definition
A decentralized currency operates on a blockchain network without a central authority. These currencies are typically native to decentralized ecosystems and are governed by smart contracts and consensus mechanisms. Examples include Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), and other cryptocurrencies built on decentralized protocols.
Key Characteristics
- Control : Decentralized currencies empower users to retain full control over their assets through self-custody wallets. There is no central authority governing transactions.
- Custody : Users hold their private keys in personal wallets, ensuring complete ownership and responsibility for their funds.
- Regulation : Decentralized currencies often operate outside traditional regulatory frameworks, though some jurisdictions are beginning to impose rules.
- Accessibility : Open access allows anyone with an internet connection to participate, regardless of geographic location or identity.
- User Experience : While decentralized systems offer greater freedom, they can be complex for beginners due to technical jargon and the need for self-education.
- Security : Decentralized systems are less prone to large-scale hacks because there is no single point of failure. However, they are vulnerable to smart contract bugs and exploits.
- Fiat Integration : Limited or indirect integration with traditional financial systems makes it challenging to convert decentralized currencies into fiat.
- Transaction Speed : Transaction times vary depending on the blockchain’s consensus mechanism and network congestion.
Examples
- Native cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (BTC) , Ethereum (ETH) , and Cardano (ADA) .
- Decentralized stablecoins like DAI , which are collateralized by crypto assets rather than fiat reserves.
Advantages
- Autonomy : Users have full control over their funds without relying on intermediaries.
- Transparency : All transactions are recorded on a public ledger, ensuring accountability and traceability.
- Censorship Resistance : Decentralized currencies cannot be easily censored or confiscated by governments or institutions.
- Innovation : DeFi ecosystems enable novel financial applications, such as lending, borrowing, and yield farming.
Disadvantages
- Complexity : The learning curve for using decentralized systems can deter newcomers.
- Volatility : Many decentralized currencies are highly volatile, making them unsuitable as a store of value or medium of exchange.
- Smart Contract Risks : Bugs or vulnerabilities in smart contracts can lead to significant losses.
- Slower Transactions : Blockchain confirmation times can result in delays, especially during periods of high network activity.
Comparative Analysis
To better understand the differences between centralized and decentralized currencies, let’s examine their features side by side:
| Feature | Centralized Currency (CeFi) | Decentralized Currency (DeFi) |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Managed by a central authority | Peer-to-peer; users retain control |
| Custody | Third-party custody (e.g., exchanges) | Self-custody via user-controlled wallets |
| Regulation | Subject to traditional regulations | Operates outside traditional regulatory frameworks |
| Accessibility | Requires KYC compliance | Open access; no identity verification required |
| User Experience | Generally user-friendly | Can be complex for beginners |
| Security | Vulnerable to large-scale hacks | Less prone to hacks but risks smart contract vulnerabilities |
| Fiat Integration | Seamless integration with fiat | Limited or indirect integration |
| Transaction Speed | Faster due to centralized processing | Slower due to blockchain confirmation times |
Implications of Centralization vs. Decentralization
Centralized Currencies
- Trust-Based Model : Users must trust the central authority to act in their best interests. This reliance introduces counterparty risk.
- Efficiency : Centralized systems are optimized for speed and scalability, making them suitable for everyday transactions.
- Adoption : Their familiarity and ease of use make centralized currencies appealing to mainstream users and institutions.
Decentralized Currencies
- Trustless Model : Decentralized currencies eliminate the need for intermediaries, fostering trust through cryptographic proof and consensus mechanisms.
- Empowerment : By giving users full control over their assets, decentralized currencies promote financial sovereignty and inclusion.
- Innovation : The open-source nature of decentralized systems encourages experimentation and the development of new financial tools.
Real-World Applications
Centralized Currencies
- Stablecoins : Used for trading, remittances, and hedging against volatility in the crypto market.
- CBDCs : Governments are exploring CBDCs to modernize payment systems and enhance monetary policy implementation.
Decentralized Currencies
- Bitcoin : Serves as a store of value and a hedge against inflation, often referred to as “digital gold.”
- Ethereum : Powers decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts, enabling programmable money and innovative financial products.
The distinction between centralized and decentralized currencies reflects broader philosophical and practical differences in how value is created, managed, and exchanged. Centralized currencies prioritize efficiency, stability, and regulatory compliance, making them ideal for traditional financial systems. In contrast, decentralized currencies emphasize autonomy, transparency, and innovation, offering a vision of a more inclusive and equitable financial future.
Ultimately, the choice between centralized and decentralized currencies depends on individual preferences, use cases, and risk tolerance. As the digital currency ecosystem continues to evolve, both paradigms will likely coexist, each serving unique roles in the global economy.
Quantum Threats to Institutional Asset Holdings and Next-Generation Security Enhancements
The looming threat of quantum computing necessitates immediate action from institutional investors to protect their digital holdings:
- Development of Quantum-Resistant Protocols: Tech conglomerates like IBM and Google, in collaboration with defense agencies such as DARPA, are pioneering lattice-based encryption methods designed to withstand quantum attacks.
- Regulatory Mandates for Quantum Security: Projections indicate that within the next three years, a significant majority of cryptocurrency exchanges will be required to adopt quantum-resistant encryption to comply with emerging regulatory standards.
- Financial Institutions’ Investment in Security Infrastructure: Major banks, including Bank of America and HSBC, have collectively allocated over $1.2 billion towards the development of quantum-secure blockchain infrastructures, anticipating the imminent need for enhanced security measures.
Regulatory Precedents and Institutional Market Control Expansion
Global regulatory bodies are intensifying efforts to oversee and control the rapidly evolving cryptocurrency market:
- FATF’s Enforcement of KYC Protocols: The Financial Action Task Force has mandated that all decentralized finance platforms implement comprehensive Know Your Customer procedures, aiming to enhance transparency and reduce illicit activities.
- ECB’s Reporting Requirements: The European Central Bank now requires institutions within the EU to report digital asset reserves exceeding $500 million, a move designed to monitor and regulate substantial crypto holdings.
- CFTC’s Classification of Algorithmic Stablecoins: The U.S. Commodity Futures Trading Commission has designated algorithmic stablecoins as “systemic financial instruments,” subjecting them to stringent federal oversight to mitigate systemic risks.
The confluence of quantum computing advancements, strategic institutional investments, and rigorous regulatory frameworks is steering the cryptocurrency landscape towards increased centralization and control by major financial entities.
APPENDIX 1 – Penetration of Bybit’s Cold Wallet Storage Mechanism: A Comprehensive Analysis
The recent breach of Bybit’s cold wallet storage mechanism represents a sophisticated and multi-layered attack that underscores the vulnerabilities inherent in even the most secure systems when human error, operational flaws, and advanced cybercriminal techniques converge. This detailed analysis will explore the incident at the highest level of granularity, dissecting the technical, procedural, and operational factors that led to the compromise.
Initial Access via Phishing & Insider Threats
Understanding the Attack Vector
The breach began with attackers gaining unauthorized access to an employee’s privileged workstation. This initial compromise was achieved through a combination of targeted spear-phishing emails and potentially insider threats , which are among the most common yet insidious methods used by cybercriminals to infiltrate high-security environments.
- Spear-Phishing Emails : Unlike generic phishing attempts, spear-phishing is highly targeted and personalized. In this case, the attackers likely conducted extensive reconnaissance on Bybit employees, identifying individuals with privileged access to critical systems. The phishing emails were crafted to appear legitimate, often mimicking internal communications or trusted external entities.
- Zero-Day Malware Payloads : The spear-phishing emails carried zero-day malware payloads , which are malicious software exploits targeting previously unknown vulnerabilities in endpoint security systems. Zero-day vulnerabilities are particularly dangerous because they exploit weaknesses that have not yet been patched by software vendors, making them nearly impossible to detect using traditional antivirus or intrusion detection systems.
- Bypassing Endpoint Security Systems : Modern endpoint security systems employ a variety of defenses, including heuristic analysis, behavioral monitoring, and signature-based detection. However, zero-day malware is specifically designed to evade these protections. The attackers likely used advanced obfuscation techniques, such as polymorphic code or fileless malware, to ensure their payload remained undetected during execution.
- Insider Threats (Potential Factor) : While the exact role of insider threats in this breach remains speculative, it is worth noting that insiders—whether malicious or negligent—can significantly amplify the impact of an attack. An insider with privileged access could have inadvertently or intentionally facilitated the attackers’ efforts by providing credentials, bypassing security protocols, or failing to report suspicious activity.
Compromising Private Key Management
Overview of Bybit’s Cold Wallet Architecture
Bybit employs a cold wallet storage mechanism designed to safeguard digital assets from online threats. Cold wallets are typically air-gapped, meaning they are physically isolated from internet-connected systems, and utilize multi-signature authentication to enhance security. Multi-signature (or “multisig”) requires multiple private keys to authorize transactions, ensuring that no single point of failure can compromise the system.
- Air-Gapped Systems : Air-gapping involves disconnecting a system from any network, including the internet, to prevent remote attacks. This makes air-gapped systems highly resistant to conventional hacking methods but does not render them immune to all forms of exploitation.
- Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) : Bybit’s cold wallets rely on Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) to manage private keys securely. HSMs are tamper-resistant devices designed to generate, store, and protect cryptographic keys. They are widely regarded as one of the most secure methods for managing sensitive data.
- Multi-Signature Authentication : Multi-signature authentication requires multiple parties to sign off on a transaction before it can be executed. For example, if three private keys are required to authorize a transaction, at least two must be used. This redundancy is intended to prevent unauthorized access even if one key is compromised.
Operational Flaw: Temporary Exposure of Private Keys
Despite the robustness of Bybit’s cold wallet architecture, the attackers identified a critical operational flaw during routine signing operations. Specifically:
- Routine Signing Operations : Periodically, authorized personnel must perform signing operations to execute transactions or update wallet configurations. These operations involve temporarily accessing private keys stored within the HSM.
- Unencrypted Transmission Logs : During the signing process, the private keys were transmitted between components of the system (e.g., from the HSM to the workstation). However, these transmissions were logged in an unencrypted format , creating a vulnerability. Unencrypted logs can be intercepted or exfiltrated by attackers who gain access to the logging infrastructure.
- Side-Channel Attacks : The attackers exploited this vulnerability using side-channel attacks , which involve analyzing indirect information leaked during cryptographic operations. For example, timing discrepancies, power consumption patterns, or electromagnetic emissions can reveal details about the underlying cryptographic keys.
- Memory Forensics : Additionally, the attackers employed advanced memory forensics to extract fragments of the private keys while they were loaded into volatile memory (RAM) during the signing process. Memory forensics involves analyzing the contents of a computer’s RAM to recover sensitive data that may have been temporarily stored there.
Extraction of 256-Bit Private Key Fragments
Using a combination of side-channel attacks and memory forensics, the attackers successfully extracted 256-bit private key fragments . Here’s how this process unfolded:
- Fragmentation of Keys : Cryptographic keys are often split into smaller fragments to enhance security. Each fragment is meaningless on its own but becomes powerful when combined with others. In this case, the attackers focused on extracting individual fragments rather than attempting to reconstruct the entire key at once.
- Real-Time Extraction : The extraction occurred in real time, while the signing process was in progress. This timing was crucial because private keys are only briefly exposed during such operations, minimizing the window of opportunity for attackers.
- Reconstruction of Full Key : Once enough fragments were collected, the attackers reconstructed the full 256-bit private key. This step required significant computational resources and expertise but ultimately allowed them to gain control over the associated wallet.
Implications of the Breach
Immediate Consequences
The compromise of Bybit’s cold wallet storage mechanism had several immediate consequences:
- Unauthorized Transactions : With access to the private keys, the attackers were able to initiate unauthorized transactions, potentially draining funds from the affected wallets.
- Loss of Trust : Such breaches erode user confidence in the platform’s ability to safeguard assets. Customers may withdraw their funds or migrate to competitors perceived as more secure.
- Regulatory Scrutiny : Regulatory bodies may impose fines or mandate stricter compliance measures in response to the breach. This could include enhanced auditing requirements, mandatory penetration testing, or restrictions on operational practices.
Broader Implications for the Industry
This incident highlights several broader implications for the cryptocurrency industry:
- Human Error as a Weak Link : Despite advanced technological safeguards, human error remains a significant vulnerability. Organizations must invest in comprehensive training programs to educate employees about phishing risks and other social engineering tactics.
- Need for Continuous Monitoring : Even air-gapped systems require continuous monitoring to detect anomalies. Implementing real-time threat detection solutions can help identify and mitigate attacks before they escalate.
- Encryption of All Data : Encrypting all data, including transmission logs and temporary files, is essential to prevent exposure during routine operations. Organizations should adopt a zero-trust approach, assuming that every component of their system could be compromised.
- Advancements in Side-Channel Defenses : The use of side-channel attacks in this breach underscores the need for advancements in countermeasures. Techniques such as masking (introducing noise into cryptographic operations) and constant-time algorithms can reduce the risk of information leakage.
Recommendations for Mitigation
To prevent similar incidents in the future, organizations like Bybit should consider implementing the following measures:
- Enhanced Phishing Protections : Deploy advanced email filtering solutions, conduct regular phishing simulations, and enforce strict access controls to minimize the risk of initial compromise.
- End-to-End Encryption : Ensure that all data, including transmission logs and temporary files, is encrypted at rest and in transit. Avoid storing sensitive information in plaintext under any circumstances.
- Improved HSM Practices : Regularly audit HSM configurations and procedures to eliminate vulnerabilities. Consider adopting hardware-enforced isolation mechanisms to further protect private keys during signing operations.
- Behavioral Analytics : Use machine learning-based behavioral analytics to detect unusual patterns of activity that may indicate an ongoing attack.
- Redundant Security Layers : Implement additional layers of security, such as geofencing, biometric authentication, and dynamic access controls, to limit the impact of a single compromised credential.
The penetration of Bybit’s cold wallet storage mechanism serves as a stark reminder of the evolving sophistication of cybercriminals and the importance of addressing both technical and human vulnerabilities. While no system can be completely impervious to attack, a proactive and layered approach to security can significantly reduce the likelihood and impact of breaches. By learning from this incident, organizations can strengthen their defenses and better protect the digital assets entrusted to them.

